STIC-model is an automatic diagnostic system for differentiating malignant hepatic tumors based on patients’ multimodal medical data including multi-phase contrast-enhanced computed tomography and clinical features. The model has modular design of SpatialExtractor-TemporalEncoder-Integration-Classifier (STIC), which takes the preprocessed multi-phase CECT images and corresponding encoded clinical features as input, and finally outputs the score for each type of malignant hepatic tumors. SpatialExtractor module is a deep CNN that uses convolutional layers to extract detailed spatial features of CECT images. TemporalEncoder module uses gated RNN to mine the changing pattern among different CECT phases. In the Integration module, the TemporalEncoder module is concatenated with the vector of encoded dummy clinical variables. Finally, in the Classifier module, the Integration output is passed through the softmax activation function to implement the classification task.
This AI-assisted diagnostic system aims to provide an easy-to-use user interface. The user only needs to upload three phase CECT images (DICOM format) and input corresponding clinical features. STIC-model online tool automatically preprocess input CECT images, including CT HU value conversion and multi-phase CT affine registration. STIC-model finally outputs the score for each type of malignant hepatic tumors.
(a) Three phase CECT DICOM files: non-contrast-enhanced phase (NC phase), arterial phase (ART phase) and portal venous phase (PV phase)
(b) Clinical features: age, gender, platelet (PLT), total bilirubin (TBIL), alpha fetoprotein (AFP), carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA125) and hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg).
STIC-model automatedly analyzes uploaded data (Three phase CECT DICOM files and coresspoding clinical features).
STIC-model outputs the predicted score for each type of malignant hepatic tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) and metastatic liver cancer (metastasis)
| Patients ID | NC phase | ART phase | PV phase | Predicted score of STIC-model |
| test006 | 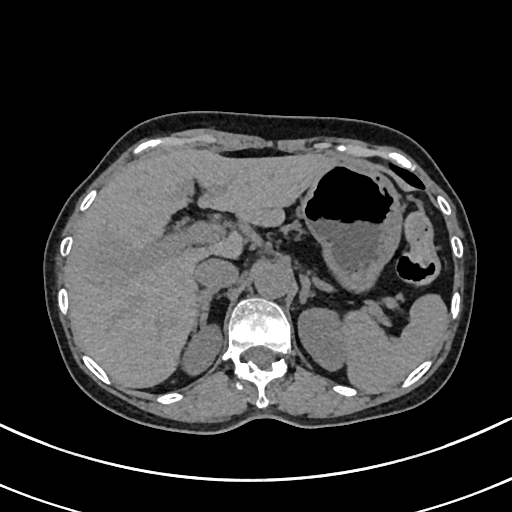 |
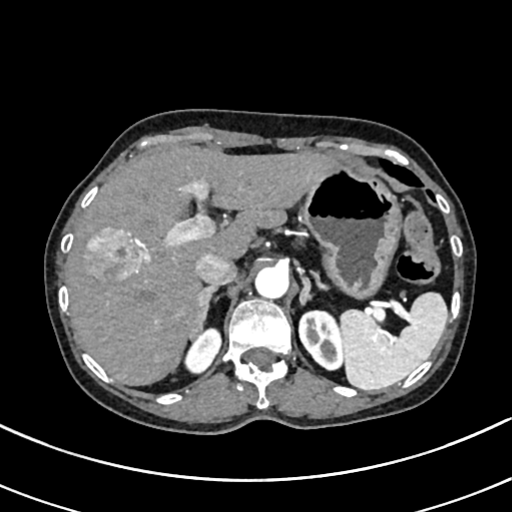 |
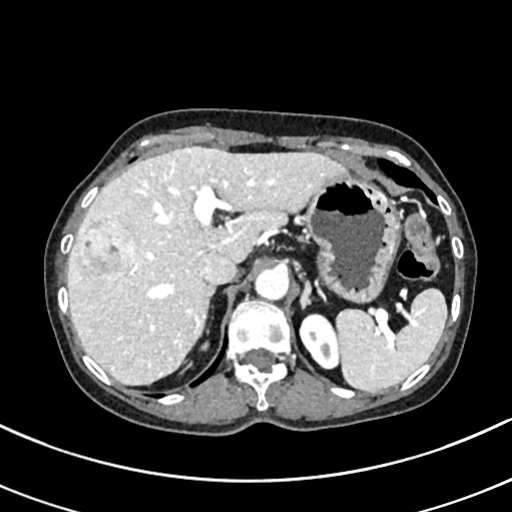 |
HCC score: 0.774 ICC score: 0.102 Metastasis score: 0.124 Diagnosis result: HCC |
| test008 | 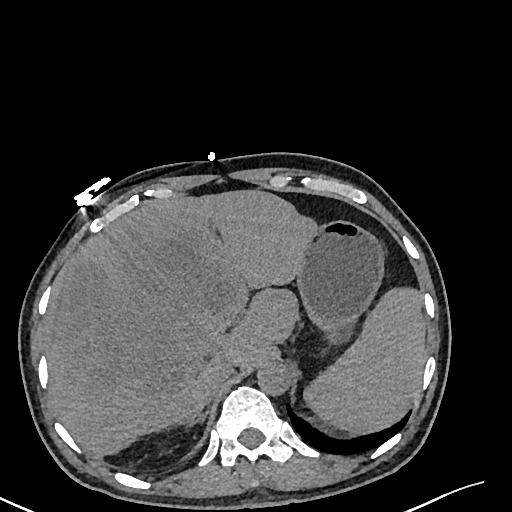 |
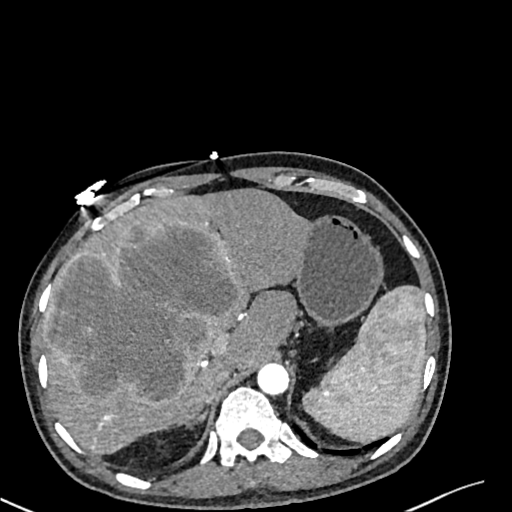 |
 |
HCC score: 0.067 ICC score: 0.646 Metastasis score: 0.287 Diagnosis result: ICC |
| test019 | 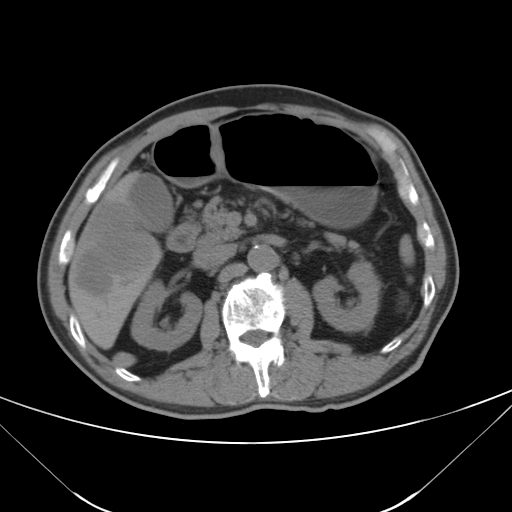 |
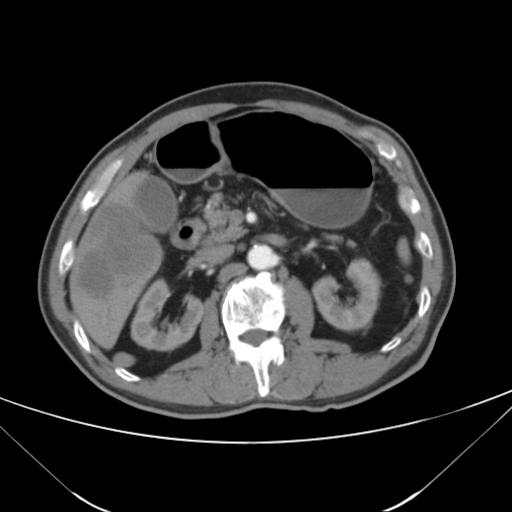 |
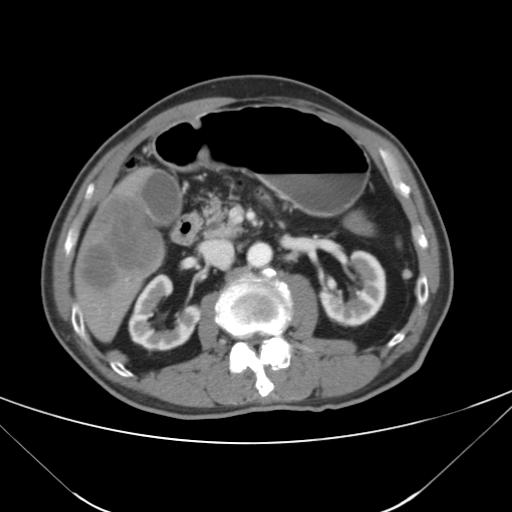 |
HCC score: 0.173 ICC score: 0.176 Metastasis score: 0.651 Diagnosis result: Metastasis |
Please cite our work if you find this STIC model helpful:
Gao, R., Zhao, S., Aishanjiang, K. et al. Deep learning for differential diagnosis of malignant hepatic tumors based on multi-phase contrast-enhanced CT and clinical data. J Hematol Oncol 14, 154 (2021). [Find the article]
Department of Bioinformatics and Biostatistics, School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Ye Jiequan Building, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai 200240, China
Author: Ruitian Gao (r.t.gao@sjtu.edu.cn)
Correspondence: Zhangsheng Yu (yuzhangsheng@sjtu.edu.cn)