A fully automated Deep convolutional network for survival prediction using the Cox Proportional-Hazard model directly from histopathological images in Stomach Cancer (DeepCox-SC). The DeepCox-SC model automatedly selects patches with more information for survival prediction. The MultiDeepCox-SC multi-modal fusion model further integrated DeepCox-SC risk score, clinical data (age), and gene expression data to improve survival prediction. The DeepCox-SC model could be utilized as a computer-assisted tool to improve pathologists' efficiency and accuracy.
This Computer-assisted tool aims to provide a simply and user-friendly usage environment. The user only needs to input the url of whole slide image (WSI). DeepCox-SC online tool automatically selected patches with the largest frequency of nuclei. DeepCox-SC finally outputs predicting patients' risk of death (DeepCox-SC risk score). DeepCox-SC multi-modal fusion model further integrated DeepCox-SC risk score, age, and gene expression data to improve survival prediction. Age and gene expression data are optional.
Input the url of WSI.
Age and gene expression data are optional.
DeepCox-SC automatedly analyze uploaded data (WSI, age, gene expression).
DeepCox-SC outputs the predicted patients' risk of death (DeepCox-SC risk score).
DeepCox-SC multi-modal fusion model further integrates DeepCox-SC risk score, age, and gene expression data and outputs the risk score
| Patients | Whole slide image (WSI) | The patch with more information for survival prediction | DeepCox-SC risk score of WSI |
| TCGA-BR-A452 | 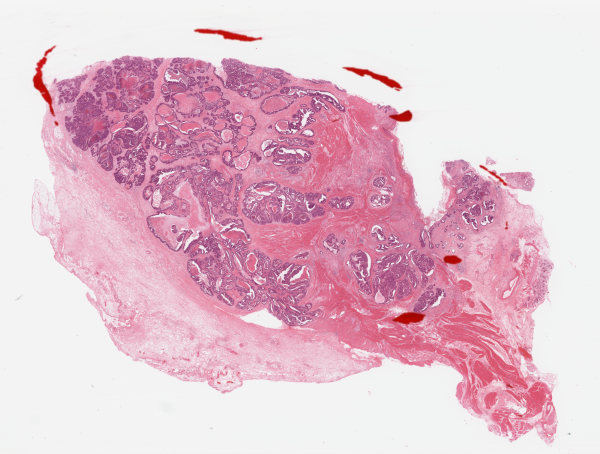 |
 |
DeepCox-SC risk score: 4.78. Group: High-risk group. 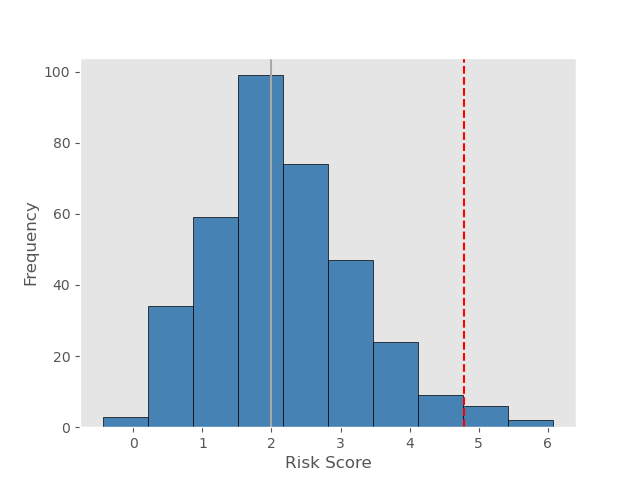 Grey line is the median of risk scores Grey line is the median of risk scores of stomach cancer patients in TCGA dataset Red line is the risk score of your input histopathological image |
Please cite our work if you find this DeepCox-SC tool helpful:
Wei T, Yuan X, Gao R, Johnston L, Zhou J, Wang Y, Xie Y, Zhang Y, Yu Z. Survival Prediction of Stomach Cancer Using Deep Learning Models with Histopathological Images and Expression Data. [Find the article]
Department of Bioinformatics and Biostatistics, School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Ye Jiequan Building, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai 200240, China
Author: Ting Wei (weitinging@sjtu.edu.cn)
Correspondence: Zhangsheng Yu (yuzhangsheng@sjtu.edu.cn)